What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where the amount of glucose in your blood is too high. This occurs when your pancreas does not produce any insulin or enough insulin. Also when the produced insulin does not work properly, this leads to diabetes. Insulin is a hormone that regulates the level of blood glucose by allowing glucose to enter cells to be used as energy throughout your body.
In the diabetic state, the concentration of glucose in the blood becomes high, which may lead to a variety of complications in various parts of the body. Unlike other chronic diseases, you can play a big part in managing your diabetes.
What Causes Diabetes?
What causes type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing 𝛽-cells in the pancreas, which usually leads to absolute insulin deficiency.
What causes type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes which is mainly caused by both genetics and environmental factors (obesity, stress, drug abuse, and lack of exercise).
Diabetes Diagnostic Standard
| Normal | Prediabetes | Type 2 Diabetes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Blood Glucose | ≤ 99 mg/dL | ≥ 100-125 mg/dL | ≥ 126 mg/dL |
| Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) | ≤ 5.6% | 5.7-6.4% | ≥ 6.5% |
| 2-hour Postprandial Glucose | < 140 mg/dL | 140-199 mg/dL | ≥ 200 mg/dL |
American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2018.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
How to test your blood glucose
1. Wash your hands with warm water and dry your hands completely
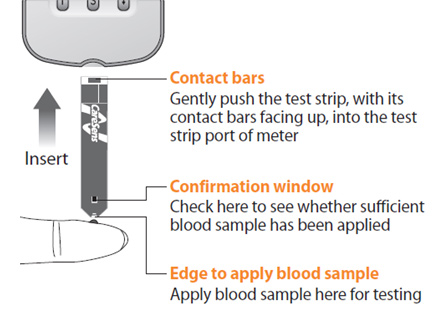
2. Insert the test strip into a meter
3. Choose a spot on your finger
4. Prick your finger with a lancing device
5. Apply a drop of blood to the inserted test strip
6. Check the confirmation window of the strip to ensure sufficient blood sample has been applied for an accurate reading
7. Read & record the blood glucose level displayed
8. Discard the lancet & used test strip